Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to Using Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagrams
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to Using Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagrams
Comprehensive Guide to Using Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagrams

Introduction
The Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram is a powerful tool for identifying and analyzing the root causes of problems, particularly in the context of customer satisfaction challenges. This guide will walk you through the process of creating and utilizing a Fishbone Diagram to address customer satisfaction issues using Visual Paradigm’s Smart Board. By the end of this guide, you will understand how to effectively use this diagram to enhance customer satisfaction and improve business dynamics.
Understanding the Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram, is a visual tool that helps in identifying potential causes of a problem. It is called a “Fishbone” Diagram because of its resemblance to the skeleton of a fish. The diagram is structured with a central spine representing the main problem, and branches representing categories of causes. Each branch can further split into smaller branches representing specific causes.
Enhancing Problem-Solving with Mind Maps
Using a mind map to model a Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram is an effective approach because both tools share a visual, hierarchical structure that is ideal for organizing and analyzing complex information. Here are several reasons why a mind map is well-suited for modeling a Fishbone Diagram:
1. Visual Representation
- Clarity: Mind maps provide a clear, visual overview of the central problem and its contributing factors. This visual representation helps in understanding the relationships between different causes and the main issue.
- Engagement: Visual elements such as colors, symbols, and images can make the diagram more engaging and easier to understand, which is beneficial for collaborative brainstorming sessions.
2. Hierarchical Structure
- Organization: Both mind maps and Fishbone Diagrams use a hierarchical structure. The central idea (the main problem) is at the center, with branches representing categories of causes and sub-branches representing specific causes.
- Detail: This structure allows for a detailed breakdown of the problem, making it easier to identify and analyze root causes at various levels of granularity.
3. Flexibility and Adaptability
- Dynamic Updates: Mind maps are flexible and can be easily updated as new information becomes available. This adaptability is crucial for ongoing problem-solving and continuous improvement processes.
- Customization: Users can customize the mind map to fit the specific needs of their analysis, adding or removing branches and sub-branches as necessary.
4. Collaborative Capabilities
- Teamwork: Mind mapping tools, such as Visual Paradigm’s Smart Board, often support real-time collaboration. This feature allows team members to work together on the diagram, contributing their insights and perspectives.
- Shared Understanding: Collaborative mind mapping ensures that all team members have a shared understanding of the problem and its causes, fostering better communication and alignment.
5. Enhanced Problem-Solving
- Root Cause Analysis: The Fishbone Diagram is specifically designed for root cause analysis. Using a mind map to model this diagram helps in systematically identifying and addressing the underlying causes of a problem.
- Comprehensive Analysis: By visually mapping out all potential causes, teams can conduct a more comprehensive analysis, ensuring that no critical factors are overlooked.
6. Integration with Other Tools
- Versatility: Mind mapping software often integrates with other tools and platforms, making it easy to incorporate the Fishbone Diagram into broader project management and problem-solving workflows.
- Export and Share: Mind maps can be easily exported and shared in various formats, facilitating communication with stakeholders who may not be directly involved in the brainstorming process.
7. Ease of Use
- Intuitive Interface: Mind mapping tools typically have an intuitive interface that makes it easy for users to create and modify diagrams. This ease of use encourages broader participation and engagement in the problem-solving process.
- Learning Curve: The learning curve for mind mapping is generally shorter compared to more complex diagramming tools, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
Using a mind map to model a Fishbone Diagram leverages the strengths of both tools, providing a visual, hierarchical, and flexible approach to problem-solving. This method enhances clarity, collaboration, and comprehensive analysis, making it an effective technique for addressing complex issues such as customer satisfaction challenges. By integrating mind maps into your problem-solving workflow, you can streamline processes, improve communication, and ensure that all team members are aligned with the goals of the analysis.
Key Categories in Customer Satisfaction Challenges
For customer satisfaction challenges, the Fishbone Diagram typically includes the following key categories:
- Product Quality
- Service Delivery
- Internal Processes
- Employee Factors
- Communication
- Technology
Steps to Create a Fishbone Diagram with Visual Paradigm Smart Board
Step 1: Access Visual Paradigm Smart Board
- Sign Up/Log In: If you don’t have an account, sign up on the Visual Paradigm website. If you already have an account, log in to access the Smart Board.
- Open Smart Board: Once logged in, navigate to the Smart Board section to start creating your Fishbone Diagram.
Step 2: Create a New Fishbone Diagram
- New Project: Click on “Create New Project” and select “Fishbone Diagram” from the available templates.
- Central Idea: Start by entering your central idea or problem in the middle of the canvas. For customer satisfaction, this could be “Customer Satisfaction Challenges.”
Step 3: Add Main Branches
- Main Branches: Add main branches that represent the key categories of customer satisfaction challenges. These include:
- Product Quality
- Service Delivery
- Internal Processes
- Employee Factors
- Communication
- Technology
Step 4: Add Sub-Branches
- Sub-Branches: Further break down each main branch into sub-branches that represent specific causes. For example, under “Product Quality,” you can add:
- Inconsistent product quality
- Defective products
- Lack of quality control measures
Step 5: Customize Your Diagram
- Use Keywords: Focus on using key phrases rather than complete sentences for each branch. This encourages concise thinking and helps in rapid idea generation.
- Incorporate Visuals: Utilize colors, symbols, and images to enhance understanding and recall. Visual elements can stimulate creativity and make the diagram more engaging.
- Hotkeys: Use hotkeys for creating diagram nodes solely with the keyboard, making the process smoother and more efficient.
Step 6: Collaborate with Your Team
- Invite Team Members: Share the diagram with your team members to gather diverse perspectives. Collaborative brainstorming can lead to unexpected insights and innovative ideas.
- Real-Time Editing: Visual Paradigm’s Smart Board allows real-time collaboration, so multiple users can work on the diagram simultaneously.
Step 7: Review and Organize
- Evaluate Causes: After generating a substantial number of causes, begin grouping similar concepts together or prioritizing key themes within your diagram.
- Adjust Plans: Update the diagram as the project evolves to reflect changes and new ideas.
Step 8: Present and Document
- Visual Presentations: Use the diagram to present information to stakeholders. Ensure clarity and engagement through visual aids.
- Documentation: Keep a record of brainstorming sessions and decisions made. This can be done directly within the Smart Board or by exporting the diagram to other formats.
Example Fishbone Diagram Structure
Here’s an example of how you might structure your Fishbone Diagram for customer satisfaction challenges:
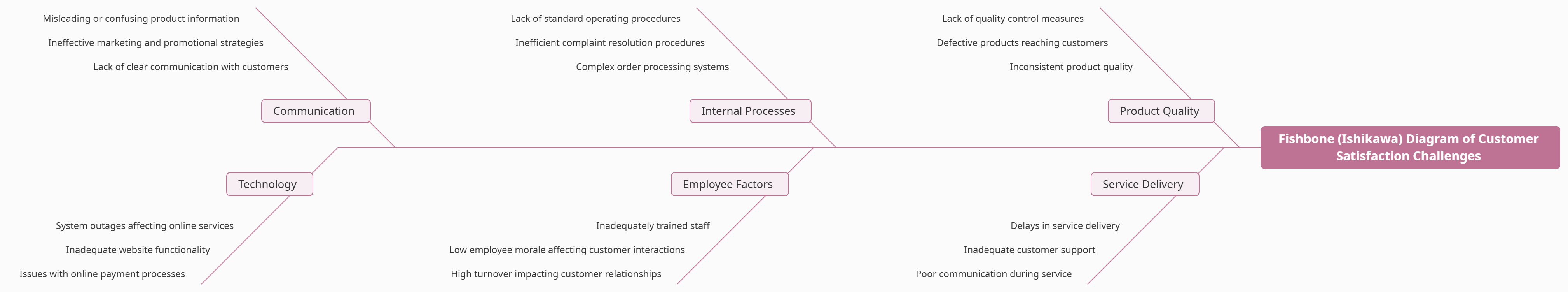
Insights from a Fishbone Analysis
The Fishbone Diagram focusing on Customer Satisfaction Challenges provides a comprehensive analysis of factors influencing the overall satisfaction of customers. By identifying and addressing issues across product quality, service delivery, internal processes, employee factors, communication, and technology, organizations can create a more positive and satisfactory customer experience.
Impact of Customer Satisfaction on Business Dynamics
Customer satisfaction is a cornerstone of business success, exerting a profound impact on various facets of an organization. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal patrons, contributing to repeat business and long-term revenue. Positive customer experiences foster brand loyalty and serve as a powerful driver for positive word-of-mouth marketing, attracting new customers through recommendations.
Benefits of Using Visual Paradigm Smart Board
- Enhanced Clarity: Provides a clear overview of tasks and their relationships.
- Improved Collaboration: Facilitates teamwork through visual representation of ideas.
- Flexibility: Easily adjustable as project requirements change.
- Effective Problem Solving: Helps in identifying challenges and brainstorming solutions.
By following these steps and utilizing Visual Paradigm’s Smart Board, you can create comprehensive and effective Fishbone Diagrams for customer satisfaction challenges, enhancing organization, collaboration, and overall project success.

