Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to Reducing Medication Errors Using the 5W’s Approach
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to Reducing Medication Errors Using the 5W’s Approach
Comprehensive Guide to Reducing Medication Errors Using the 5W’s Approach
Comprehensive Guide to Reducing Medication Errors Using the 5W’s Approach
Introduction
Medication errors are a significant concern in healthcare, posing risks to patient safety and health outcomes. Addressing these errors requires a collaborative and systematic approach involving all stakeholders. This guide explores the 5W’s (Who, What, Where, When, and Why) for reducing medication errors, providing a comprehensive framework for healthcare professionals, institutions, regulatory bodies, and patients.

Key Concepts
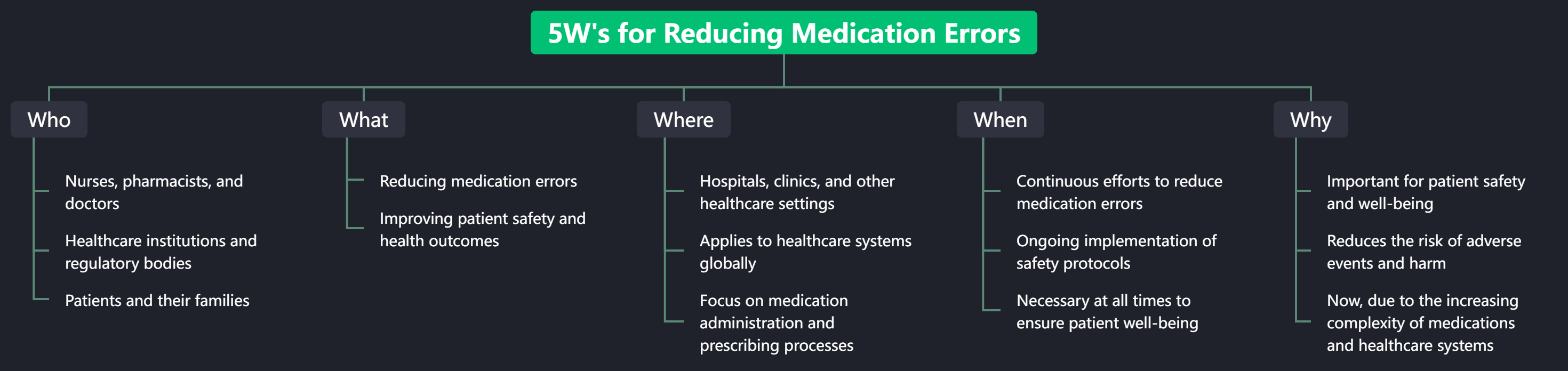
Who
Healthcare Professionals
- Nurses: Play a crucial role in administering medications and monitoring patient responses.
- Pharmacists: Ensure the accuracy of prescriptions and provide medication counseling.
- Doctors: Prescribe medications and oversee patient care.
Healthcare Institutions and Regulatory Bodies
- Hospitals and Clinics: Implement policies and procedures to minimize medication errors.
- Regulatory Bodies: Establish guidelines and standards for medication safety.
Patients and Their Families
- Patient Involvement: Encourage patients to ask questions and understand their medications.
- Family Support: Families can help monitor medication use and report any discrepancies.
What
Reducing Medication Errors
- Goal: Minimize errors in medication administration and prescribing.
- Patient Safety: Improve safety measures to prevent adverse events.
- Health Outcomes: Enhance overall health outcomes through accurate medication management.
Where
Healthcare Settings
- Hospitals: Implement robust systems for medication administration and monitoring.
- Clinics: Ensure accurate prescribing and patient education.
- Other Medical Facilities: Maintain high standards of medication safety.
Global Healthcare Systems
- International Standards: Adopt best practices from global healthcare systems.
- Collaboration: Share knowledge and resources across borders to improve medication safety.
Medication Administration and Prescribing Processes
- Standardization: Use standardized protocols for medication administration.
- Technology: Leverage technology such as electronic health records (EHRs) and barcode scanning.
When
Continuous Efforts
- Ongoing Initiatives: Continuously review and improve medication safety protocols.
- Regular Training: Provide ongoing training for healthcare professionals on medication safety.
Implementation of Safety Protocols
- Immediate Action: Implement safety protocols promptly to address identified risks.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of safety protocols and make necessary adjustments.
Vigilance
- Constant Awareness: Maintain a high level of awareness and vigilance to prevent medication errors.
- Incident Reporting: Encourage reporting of near-misses and errors to identify areas for improvement.
Why
Patient Safety and Well-being
- Importance: Ensuring patient safety is paramount in healthcare.
- Adverse Events: Reduce the risk of adverse events and harm related to medication use.
Complexity of Healthcare Systems
- Increasing Complexity: The growing complexity of medications and healthcare systems necessitates heightened attention to medication safety.
- Collaborative Efforts: Addressing medication errors requires a collaborative effort from all stakeholders.
Insights from the Mind Map
The mind map underscores the collaborative responsibility of healthcare professionals, institutions, regulatory bodies, and patients in mitigating medication errors. It emphasizes the need for continuous efforts, implementation of safety measures, and heightened awareness due to the evolving complexities of healthcare. The ultimate goal is to enhance patient safety, minimize adverse events, and optimize health outcomes through a comprehensive approach that involves all stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem.
Creating Mind Maps with Visual Paradigm Smart Board
Visual Paradigm Smart Board offers a versatile and intuitive platform for creating impactful mind maps. This online mind map software serves as an effective mind map maker and brainstorming tool, providing a collaborative space for healthcare professionals, institutions, and patients alike. Through its user-friendly interface, this mind map app facilitates the visualization of complex concepts, such as the comprehensive strategies outlined for reducing medication errors. The tool’s online capabilities enable real-time collaboration, making it an ideal choice for fostering teamwork and communication among healthcare stakeholders. With features tailored for brainstorming and strategic planning, Visual Paradigm Smart Board contributes to the continuous improvement of healthcare processes by offering a seamless and accessible way to map out ideas and initiatives.
Visual Paradigm Smart Board is a powerful tool for collaborative brainstorming and mind mapping. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it to brainstorm all the factors contributing to medication errors, organized by the 5W’s (Who, What, Where, When, Why).
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Setting Up the Smart Board
Create a New Mind Map
- Open Visual Paradigm Smart Board: Log in to your Visual Paradigm account and open the Smart Board application.
- Create a New Mind Map: Click on “Create” and select “Mind Map” from the available templates.
Define the Central Topic
- Central Node: Set the central node as “Factors Contributing to Medication Errors.”
2. Brainstorming Using the 5W’s
Who
-
Healthcare Professionals
- Nurses:
- Workload and fatigue
- Training and education
- Communication with other healthcare professionals
- Pharmacists:
- Verification processes
- Work environment
- Interaction with prescribers
- Doctors:
- Prescribing habits
- Knowledge of medications
- Communication with patients
- Nurses:
-
Healthcare Institutions and Regulatory Bodies
- Policies and Procedures:
- Clarity and accessibility
- Enforcement and monitoring
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Adherence to standards
- Inspection and audits
- Policies and Procedures:
-
Patients and Their Families
- Patient Education:
- Understanding of medications
- Adherence to instructions
- Family Support:
- Monitoring and assistance
- Communication with healthcare providers
- Patient Education:
What
-
Types of Medication Errors
- Dosage errors
- Wrong medication
- Administration errors
- Documentation errors
-
Impact on Patient Safety and Health Outcomes
- Adverse drug reactions
- Prolonged hospital stays
- Increased healthcare costs
Where
-
Healthcare Settings
- Hospitals:
- Ward environment
- Emergency departments
- Intensive care units
- Clinics:
- Outpatient settings
- Specialty clinics
- Other Medical Facilities:
- Nursing homes
- Rehabilitation centers
- Hospitals:
-
Global Healthcare Systems
- Variations in healthcare practices
- Resource availability
- Cultural factors
-
Medication Administration and Prescribing Processes
- Manual vs. automated systems
- Use of technology (e.g., EHRs, barcode scanning)
- Standardization of processes
When
-
Continuous Efforts
- Regular training and education
- Ongoing monitoring and evaluation
-
Implementation of Safety Protocols
- Immediate response to incidents
- Regular updates to protocols
-
Vigilance
- Constant awareness and reporting
- Incident analysis and learning
Why
-
Patient Safety and Well-being
- Importance of preventing harm
- Enhancing quality of care
-
Complexity of Healthcare Systems
- Increasing complexity of medications
- Interactions between different healthcare systems
-
Current Relevance
- Growing awareness of medication errors
- Advancements in healthcare technology
3. Organizing the Mind Map
Create Branches for Each “W”
- Who: Branch out to healthcare professionals, institutions, and patients.
- What: Branch out to types of errors and their impacts.
- Where: Branch out to different healthcare settings and global considerations.
- When: Branch out to continuous efforts, safety protocols, and vigilance.
- Why: Branch out to patient safety, complexity, and current relevance.
Add Sub-Branches for Detailed Factors
- Healthcare Professionals: Add sub-branches for nurses, pharmacists, and doctors.
- Types of Errors: Add sub-branches for dosage errors, wrong medication, etc.
- Healthcare Settings: Add sub-branches for hospitals, clinics, and other facilities.
- Continuous Efforts: Add sub-branches for training, monitoring, and evaluation.
4. Collaborative Brainstorming
Invite Team Members
- Collaboration: Invite healthcare professionals, administrators, and other stakeholders to the Smart Board.
- Real-Time Editing: Allow team members to add their insights and ideas in real-time.
Discuss and Refine
- Discussion: Use the chat and comment features to discuss each factor.
- Refinement: Refine the mind map based on the collective input.
5. Finalizing the Mind Map
Review and Validate
- Review: Review the mind map to ensure all factors are covered.
- Validation: Validate the factors with evidence and data.
Export and Share
- Export: Export the mind map in various formats (PDF, image, etc.).
- Share: Share the mind map with the broader team and stakeholders for further action.
Conclusion
Reducing medication errors is a critical aspect of enhancing patient safety and health outcomes. By addressing the 5W’s (Who, What, Where, When, and Why), healthcare professionals, institutions, regulatory bodies, and patients can collaboratively work towards minimizing errors and improving medication management. Utilizing tools like mind maps and collaborative platforms can further enhance communication, planning, and implementation of safety measures, ultimately leading to better healthcare outcomes.
Using Visual Paradigm Smart Board to brainstorm the factors contributing to medication errors is an effective way to engage all stakeholders and ensure a comprehensive approach to improving medication safety. By organizing the factors using the 5W’s framework, you can systematically address each aspect and develop targeted strategies to reduce medication errors.

