Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) with Visual Paradigm
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) with Visual Paradigm
Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) with Visual Paradigm
Introduction to BPMN
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized graphical representation used to model business processes. It is essential for businesses seeking to improve efficiency, enhance communication, and streamline operations across various departments. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of BPMN, its components, and its applications, with a focus on using Visual Paradigm for effective BPMN modeling.

What is BPMN?
BPMN stands for Business Process Model and Notation. It was initially developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) in 2004 and has since been maintained by the Object Management Group (OMG) following their merger in 2005. The most recent version, BPMN 2.0, was released in January 2011, introducing execution semantics alongside the existing notational elements, making it a robust tool for both business analysts and technical developers.
Objectives of BPMN
The primary goals of BPMN include:
- Standardization: Providing a common language for all stakeholders involved in business processes, including business analysts, technical developers, and managers.
- Clarity: Offering an intuitive notation that can represent complex process semantics while remaining accessible to non-technical users.
- Integration: Facilitating communication between business process design and implementation to avoid gaps in understanding.
Components of BPMN
BPMN diagrams use standardized symbols to represent various elements of business processes. Key components include:

Flow Objects
- Events: Represent something that happens during a process (e.g., start, end).
- Activities: Tasks performed within the process.
- Gateways: Decision points that determine the path of the process flow.
Connecting Objects
- Sequence Flows: Indicate the order of activities.
- Message Flows: Show communication between participants.
- Association: Links artifacts with flow objects.
Swimlanes
- Pools: Represent major participants in a process (e.g., organizations).
- Lanes: Subdivisions within pools that categorize responsibilities.
Artifacts
Additional information such as data objects or annotations that provide context to the process.
Creating a BPMN Diagram
To create an effective BPMN diagram:
- Identify the Process: Clearly define the business process you wish to model.
- Gather Information: Collaborate with stakeholders to collect necessary details about tasks, decisions, and interactions involved.
- Select Tools: Utilize BPMN-compliant software tools like Visual Paradigm for diagram creation.
- Draft the Diagram:
- Start with events to mark the beginning and end of the process.
- Add activities and connect them using sequence flows.
- Incorporate gateways for decision points.
- Use swimlanes to clarify roles and responsibilities.
- Review and Revise: Share the draft with stakeholders for feedback and make necessary adjustments for clarity and accuracy.
Applications of BPMN
BPMN diagrams are widely used across industries for:
- Process Documentation: Providing a clear visual representation of processes for training and reference.
- Process Improvement: Identifying inefficiencies or bottlenecks within workflows to enhance operational performance.
- Compliance and Auditing: Ensuring processes adhere to regulatory standards by documenting workflows accurately.
- Collaboration: Facilitating discussions among teams by providing a common visual language that everyone can understand.
Using Visual Paradigm for BPMN
Visual Paradigm is a highly recommended tool for Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) due to its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface. Here are the key aspects that make Visual Paradigm an excellent choice for BPMN modeling:
Key Features of Visual Paradigm for BPMN
- Comprehensive Modeling Support: Visual Paradigm supports multiple modeling notations, including BPMN, UML, and ERD. This flexibility allows users to select the most suitable notation for their specific needs, particularly emphasizing BPMN for detailed business process modeling.
- User-Friendly BPMN Editor: The intuitive BPMN editor features drag-and-drop functionality, enabling users to quickly create process diagrams. Users can easily manage complexity by expanding or collapsing subprocess shapes, making it simple to visualize both high-level processes and detailed workflows.
- Process Simulation and Analysis: Visual Paradigm allows users to simulate business processes to identify potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies before implementation. This proactive approach helps organizations refine processes, leading to improved operational efficiency.
- Reporting and Documentation: The tool includes features for generating detailed reports based on modeled processes. This capability is essential for compliance documentation and training purposes, ensuring accurate records of business processes.
- Collaboration Tools: Visual Paradigm facilitates real-time collaboration among team members, enhancing communication and alignment throughout the modeling process. This feature is crucial for teams working on complex projects where multiple stakeholders are involved.
- Glossary Management: To maintain consistent terminology across all models, Visual Paradigm provides glossary management tools. This ensures clarity in communication among team members and stakeholders.
- Resource Catalog: Users can create a resource catalog to manage resources associated with various business processes, allowing for better planning and allocation of assets.
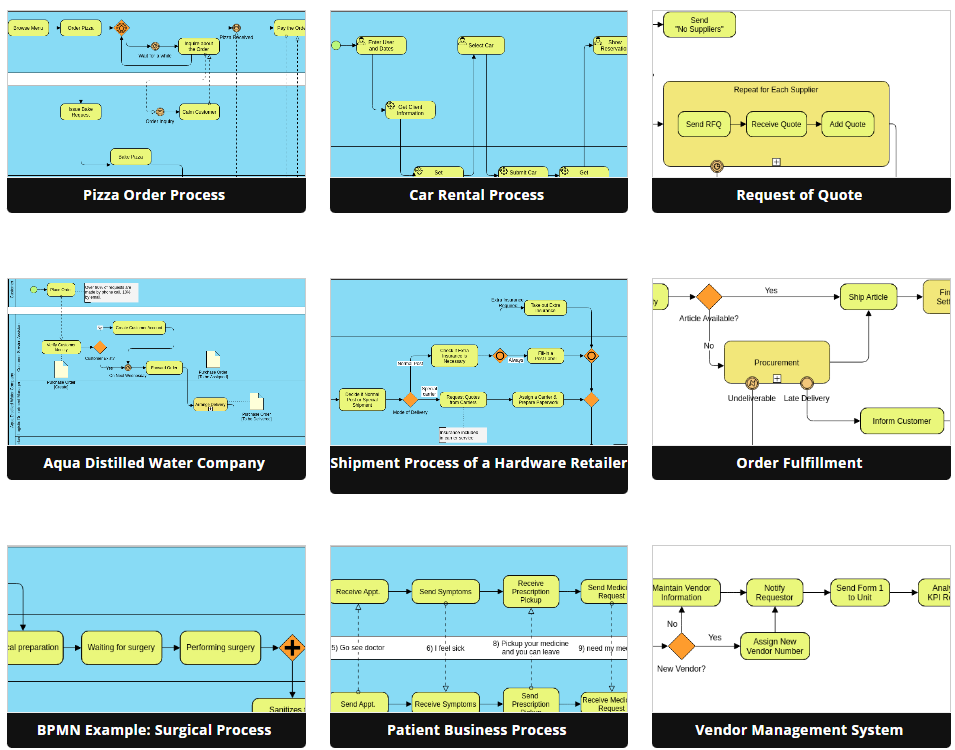
Benefits of Using Visual Paradigm for BPMN
- Enhanced Clarity: The visual representation of processes aids in understanding complex workflows, making it accessible to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Integration Capabilities: Visual Paradigm integrates seamlessly with other software systems, enhancing functionality and maintaining a cohesive workflow across different platforms.
- Animation and Simulation Features: The ability to animate process flows helps in studying resource consumption and evaluating costs throughout the execution of business processes. This feature aids in identifying bottlenecks effectively.
Conclusion
BPMN serves as a vital tool for organizations aiming to optimize their business processes through clear visualization and standardized notation. By adopting BPMN, businesses can bridge communication gaps between technical teams and business stakeholders, ultimately enhancing collaboration and efficiency across operations. Visual Paradigm’s BPMN tool stands out as a powerful solution for organizations looking to streamline their business process modeling efforts. Its comprehensive support for various modeling notations, user-friendly interface, collaboration capabilities, and advanced simulation features make it an ideal choice for effective business process management. By utilizing Visual Paradigm, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency and improve communication among stakeholders.
BPMN References
- Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm for Business Process Modeling
- Streamlining Business Processes with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Business Process Modeling Software
- Visual Paradigm: Your Comprehensive Solution for Integrated Enterprise Modeling
- Demystifying BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
- Navigating Business Processes with BPMN: A Visual Odyssey
- Visual Paradigm: The Ultimate All-in-One Visual Modeling Platform for Enterprise Architecture and Software Design
- Top Visual Paradigm Tools for Business Process Modeling
- Visual Paradigm: The Premier Tool for ArchiMate EA Modeling
- Mastering Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tool: A Step-by-Step Learning Guide
- Simplify Business Process Modeling with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tools
- BPMN — Quick Guide
- BPMN in a Nutshell — with Free Online BPMN Tool & Examples
- A Comprehensive Guide to BPMN
- Modeling As-Is and To-Be Processes
- How to Perform Gap Analysis with BPMN?
- Visual Paradigm: A Comprehensive Suite for IT Project Development and Digital Transformation

