Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
Introduction to BPMN
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a visual modeling language designed for business analysis and specifying enterprise process workflows. It serves as an open standard notation for graphical flowcharts that define business process workflows. BPMN is widely used due to its intuitive nature, making it accessible to various stakeholders, including business users, analysts, software developers, and data architects.
History of BPMN
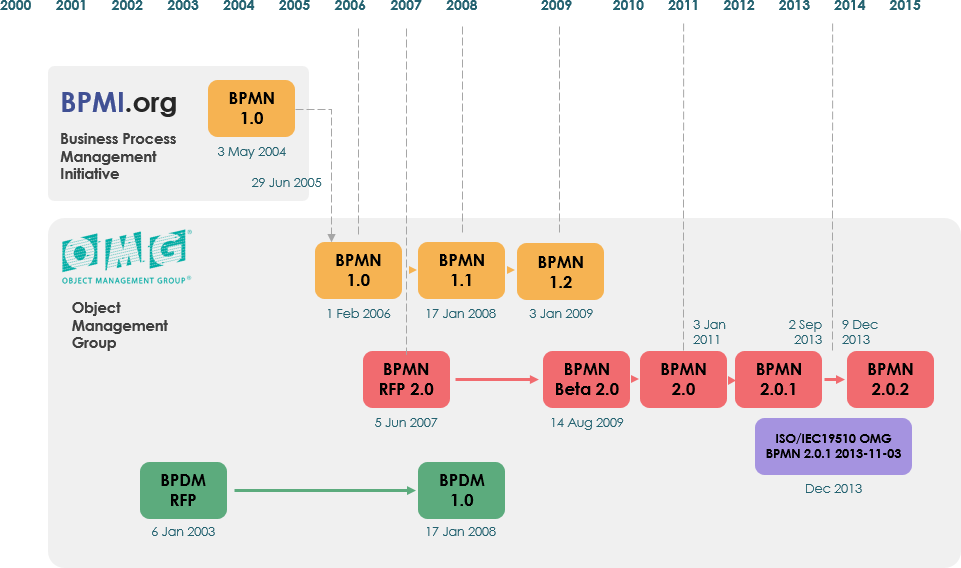
BPMN was originally developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) in 2004. After BPMI merged with the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2005, OMG took over the maintenance of BPMN. The first BPMN Specification document was released by OMG in February 2006. Version 2.0 was introduced in 2010, and the latest version, BPMN 2.0.2, was formally published by ISO as the 2013 edition standard: ISO/IEC 19510.
Benefits of BPMN
BPMN offers several key benefits:
- Standardization: It is an industry standard developed by the OMG consortium.
- Clarity: Provides businesses with the capability to define and understand their procedures through Business Process Diagrams (BPDs).
- Communication: Bridges the gap between business process design and implementation, ensuring all stakeholders understand the processes.
- Simplicity and Power: Easy to learn yet powerful enough to depict complex business processes.
Goals of BPMN
BPMN aims to support various roles within an organization:
- Technical Experts: Responsible for process implementation.
- Business Analysts: Create and improve processes.
- Managers: Monitor and control processes.
Overview of BPMN
Understanding how a business operates is crucial for process improvement. BPMN provides a graphical representation of business workflows, making it easier for analysts and stakeholders to understand and analyze processes. Each process in BPMN is represented as a series of steps (activities) performed sequentially or concurrently according to business rules.
BPMN Notation
BPMN uses diagrams with graphic elements to describe processes. These visual presentations make it easy for users to understand the logic of a process. The elements are categorized to facilitate recognition and use.
Basic Constructs
BPMN elements are divided into five basic categories:
- Swimlanes: Graphical containers representing process participants.
- Flow Elements: Elements that connect to form business workflows, including Events, Activities, and Gateways.
- Connecting Objects: Connectors that link flow objects, such as Sequence Flows, Message Flows, Associations, and Data Associations.
- Data: Information needed or produced during a business process, including Data Objects, Data Inputs, Data Outputs, and Data Stores.
- Artifacts: Additional information that does not affect the flow, such as Groups and Text Annotations.
Swimlanes
Swimlanes are rectangular boxes representing participants in a business process. They can be arranged horizontally or vertically and contain flow objects performed by the participant. There are two types of swimlanes:

- Pools: Represent participants like departments or roles.
- Lanes: Sub-partitions of pools, representing specific entities or roles within a pool.

Activities
Activities are works performed within a business process, shown as rounded rectangles. There are two types:

- Tasks: Atomic works that cannot be further broken down.
- Sub-Processes: Complex works that can be elaborated into smaller tasks.
Events
Events are occurrences that may impact a business process, shown as circles. There are three types:

- Start Event: Indicates the beginning of a process.
- Intermediate Event: Drives the business flow based on specified conditions.
- End Event: Marks the completion of a process.

Gateways
Gateways control the flow of a business process based on conditions, shown as diamond shapes. Types include:
- Exclusive Gateway: Controls flow based on given process data.
- Inclusive Gateway: Creates parallel paths based on conditions.

- Parallel Gateway: Executes parallel flows without checking conditions.

- Event-Based Gateway: Models alternative paths based on events.

Connecting Objects
Connecting objects link flow elements:
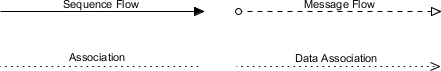
- Sequence Flows: Connect flow elements within the same pool.

- Message Flows: Show communication between pools.
Data
Data objects represent information produced or needed during a business process. Types include:

- Data Objects: General data.
- Data Inputs: Data required for a process.
- Data Outputs: Data produced by a process.
- Data Stores: Persistent data storage.
Artifacts
Artifacts provide additional information without affecting the flow:
- Groups: Categorize shapes.

- Text Annotations: Add details to flow objects.

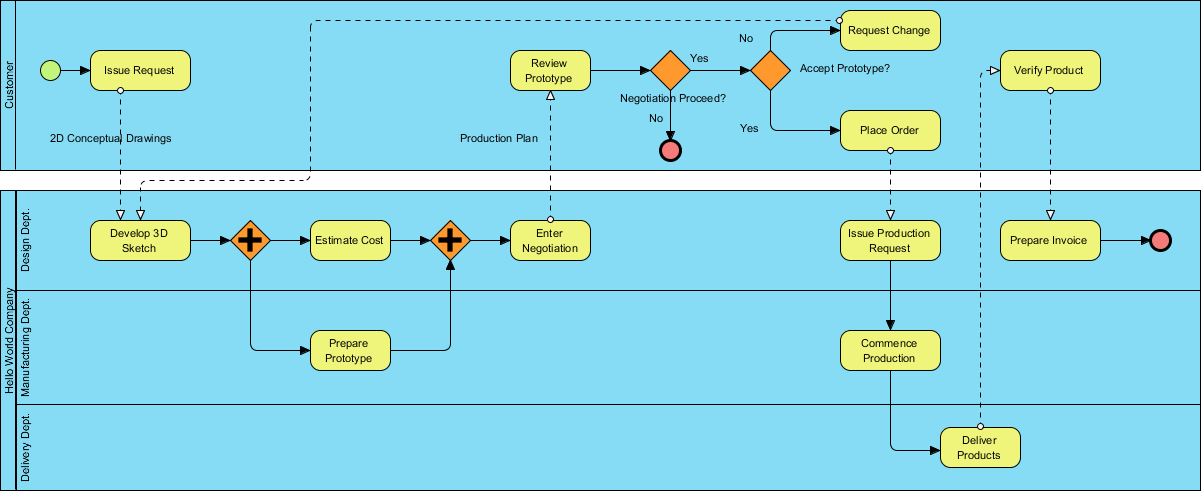
BPMN Example
Consider a distilled water company aiming to improve its ordering process. The BPMN diagram would illustrate the steps from order placement to delivery, including customer interactions, order processing, and logistics.
This Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) diagram illustrates the distilled water ordering process for The True Aqua Distilled Water Company. The process involves several key steps and participants, each represented within specific swimlanes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the diagram:

Swimlanes and Participants
- Customer: Represents the actions performed by the customer.
- Customer Service Assistant: Handles customer interactions and order processing.
- Logistics Department Manager: Responsible for arranging the delivery of orders.
- Worker: Delivers the distilled water to customers.
Process Flow
-
Place Order:
- The process begins with the customer placing an order.
- Over 90% of requests are made by phone call, with 10% by email.
-
Verify Customer Identity:
- The Customer Service Assistant verifies the customer’s identity.
- If the customer does not exist in the system, a new customer account is created.
-
Create Customer Account:
- If the customer is new, the Customer Service Assistant creates a customer account.
-
Forward Order:
- On the next Wednesday, the Customer Service Assistant forwards the orders to the Logistics Department for delivery.
-
Arrange Delivery:
- The Logistics Department Manager receives the orders and arranges the delivery by assigning workers and printing the delivery schedule.
-
Deliver Water:
- The worker delivers the distilled water to the customer based on the assigned schedule.
Artifacts
- Text Annotation:
- Provides additional information about the order placement method, indicating that over 90% of requests are made by phone call and 10% by email.
Data Objects
-
Purchase Order [To be Assigned]:
- Represents the order that needs to be assigned for delivery.
-
Purchase Order [To be Delivered]:
- Represents the order that is ready to be delivered.
-
Purchase Order [Completed]:
- Indicates that the order has been successfully delivered.
Gateways
- Customer Exist?:
- A decision point where the process checks if the customer already exists in the system.
- If yes, the order is processed directly. If no, a new customer account is created before processing the order.
Events
-
Start Event:
- The process begins with the customer placing an order.
-
Intermediate Event:
- The order is forwarded to the Logistics Department on the next Wednesday.
-
End Event:
- The process concludes with the delivery of the water to the customer.
The diagram effectively captures the entire ordering and delivery process, from the customer placing an order to the final delivery. It includes key decision points, data objects, and the flow of activities across different participants, ensuring a clear and structured representation of the business process.
Conclusion
The Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) diagram for The True Aqua Distilled Water Company provides a comprehensive and detailed visualization of the distilled water ordering and delivery process. By breaking down the process into clear, sequential steps and assigning responsibilities to specific participants, the diagram ensures that all stakeholders can easily understand and follow the workflow.
The use of swimlanes effectively organizes the process by separating the actions of different participants, including the Customer, Customer Service Assistant, Logistics Department Manager, and Worker. This separation helps in identifying the roles and responsibilities of each participant, facilitating better coordination and accountability.
The inclusion of gateways, such as the decision point for verifying customer identity, highlights the critical decision-making steps in the process. This ensures that the process can adapt to different scenarios, such as creating a new customer account if the customer does not already exist.
The diagram also incorporates essential data objects, such as purchase orders at different stages (to be assigned, to be delivered, and completed), which are crucial for tracking the progress of orders. These data objects provide a clear trail of the order status, ensuring transparency and traceability throughout the process.
Artifacts, such as text annotations, add valuable context to the diagram. For instance, the annotation indicating that over 90% of requests are made by phone call and 10% by email provides insights into customer behavior, which can be useful for process optimization and customer service improvements.
Overall, the BPMN diagram serves as a powerful tool for process improvement and standardization. It helps the company identify potential bottlenecks, streamline operations, and enhance efficiency. By providing a clear and structured representation of the business process, the diagram facilitates better communication and collaboration among stakeholders, ultimately contributing to the company’s goal of increasing market share and customer satisfaction.
In summary, the BPMN diagram for The True Aqua Distilled Water Company is a testament to the effectiveness of BPMN in modeling and improving business processes. It provides a roadmap for the company to achieve its objectives of increased operating efficiency and higher customer satisfaction, ensuring a smoother and more efficient distilled water ordering and delivery process.
- Mastering Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tool: A Step-by-Step Learning Guide
- Simplify Business Process Modeling with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tools
- BPMN — Quick Guide
- BPMN in a Nutshell — with Free Online BPMN Tool & Examples
- A Comprehensive Guide to BPMN
- Modeling As-Is and To-Be Processes
- How to Perform Gap Analysis with BPMN?
- Visual Paradigm: A Comprehensive Suite for IT Project Development and Digital Transformation
- Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm for Business Process Modeling
- Streamlining Business Processes with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Business Process Modeling Software
- Visual Paradigm: Your Comprehensive Solution for Integrated Enterprise Modeling
- Demystifying BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
- Navigating Business Processes with BPMN: A Visual Odyssey
- Visual Paradigm: The Ultimate All-in-One Visual Modeling Platform for Enterprise Architecture and Software Design
- Top Visual Paradigm Tools for Business Process Modeling
- Visual Paradigm: The Premier Tool for ArchiMate EA Modeling
- Introduction to BPMN Part I – Visual Paradigm
- BPMN Tutorial with Example – The Leave Application Process
- How to Draw BPMN Diagram?
- BPMN Activity Types Explained
- How to Create BPMN Diagram?
- How to Develop As-Is and To-Be Business Process?
- How to Draw BPMN 2.0 Business Process Diagram?
- Introduction to BPMN Part IV – Data and Artifacts
- Introduction to BPMN Part III – Flow and Connecting Objects
- How to Draw BPMN Conversation Diagram?
- Business Process Diagram Example: Sequence
- Business Process Diagram Example: The Nobel Prize


