Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to BPMN Activity Notation
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to BPMN Activity Notation
Comprehensive Guide to BPMN Activity Notation
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized graphical notation for modeling business processes. It provides a visual representation that is easy to understand and communicate, making it a valuable tool for business analysts, process designers, and stakeholders. This guide will focus on the activity notation in BPMN, based on the provided image.
Activities in BPMN
Activities represent work that is performed within a business process. They are depicted as rounded rectangles and can be categorized into different types based on their behavior and purpose.
Types of Activities
-
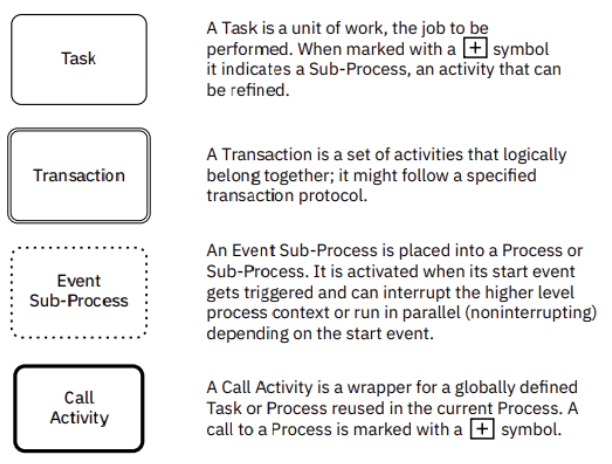
Task
- Description: A unit of work, the job to be performed.
- Icon: Rounded rectangle.
- Sub-Process Indicator: When marked with a “+” symbol, it indicates a Sub-Process, an activity that can be refined.
-
Transaction
- Description: A set of activities that logically belong together; it might follow a specified transaction protocol.
- Icon: Rounded rectangle with a double border.
-
Event Sub-Process
- Description: An Event Sub-Process is placed into a Process or Sub-Process. It is activated when its start event gets triggered and can interrupt the higher-level process context or run in parallel (non-interrupting) depending on the start event.
- Icon: Rounded rectangle with a dashed border.
-
Call Activity
- Description: A Call Activity is a wrapper for a globally defined Task or Process reused in the current Process. A call to a Process is marked with a “+” symbol.
- Icon: Rounded rectangle with a bold border.
Activity Markers
Markers indicate the execution behavior of activities. They are placed at the bottom of the activity shape.

-
Sub-Process Marker
- Icon: “+” symbol.
- Description: Indicates that the activity is a Sub-Process.
-
Loop Marker
- Icon: Circular arrow.
- Description: Indicates that the activity is a loop.
-
Parallel MI Marker
- Icon: Three vertical lines.
- Description: Indicates that the activity is a parallel multiple instance.
-
Sequential MI Marker
- Icon: Three horizontal lines.
- Description: Indicates that the activity is a sequential multiple instance.
-
Ad Hoc Marker
- Icon: Tilde (~) symbol.
- Description: Indicates that the activity is ad hoc.
-
Compensation Marker
- Icon: Arrow pointing to the left.
- Description: Indicates that the activity is a compensation activity.
Task Types
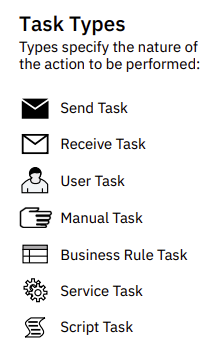
Task types specify the nature of the action to be performed. They are represented by different icons within the task shape.
-
Send Task
- Icon: Envelope with an arrow pointing out.
- Description: Represents sending a message.
-
Receive Task
- Icon: Envelope with an arrow pointing in.
- Description: Represents receiving a message.
-
User Task
- Icon: Person icon.
- Description: Represents a task performed by a user.
-
Manual Task
- Icon: Hand icon.
- Description: Represents a task that is performed manually.
-
Business Rule Task
- Icon: Document with a checkmark.
- Description: Represents a task that involves applying business rules.
-
Service Task
- Icon: Gear icon.
- Description: Represents a task that involves calling a service.
-
Script Task
- Icon: Document with a script icon.
- Description: Represents a task that involves executing a script.
Flow Types
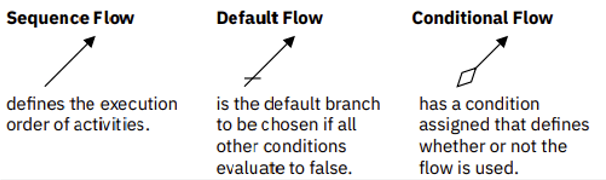
Flow types define the order and conditions of activity execution.
-
Sequence Flow
- Icon: Solid arrow.
- Description: Defines the execution order of activities.
-
Default Flow
- Icon: Solid arrow with a slash.
- Description: The default branch to be chosen if all other conditions evaluate to false.
-
Conditional Flow
- Icon: Solid arrow with a diamond shape.
- Description: Has a condition assigned that defines whether or not the flow is used.
Example
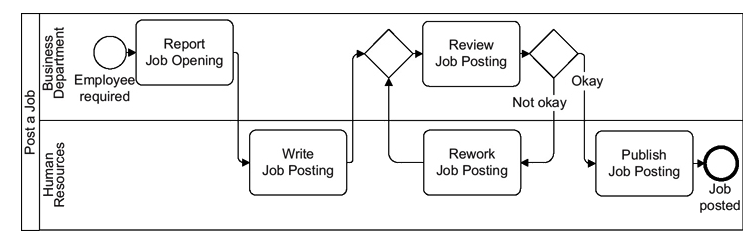
This Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) diagram depicts the process of posting a job. The diagram is divided into two lanes: “Business Department” and “Human Resources.” Each lane represents the responsibilities and activities performed by different departments in the job posting process.
Interpretation of the BPMN Diagram
-
Start Event (Business Department):
- Event: “Employee required”
- Description: The process begins when there is a need for a new employee.
-
Task (Business Department):
- Task: “Report Job Opening”
- Description: The Business Department reports the job opening to the Human Resources Department.
-
Task (Human Resources):
- Task: “Write Job Posting”
- Description: The Human Resources Department writes the job posting based on the information provided by the Business Department.
-
Exclusive Gateway (Human Resources):
- Gateway: Decision point to review the job posting.
- Description: The process splits into two paths based on whether the job posting is okay or needs to be reworked.
-
Task (Human Resources):
- Task: “Review Job Posting”
- Description: The job posting is reviewed to ensure it meets the required standards.
-
Exclusive Gateway (Human Resources):
- Gateway: Decision point based on the review.
- Description: If the job posting is okay, it proceeds to the next step. If not, it goes back for rework.
-
Task (Human Resources):
- Task: “Rework Job Posting”
- Description: If the job posting is not okay, it is reworked based on the feedback from the review.
-
Task (Human Resources):
- Task: “Publish Job Posting”
- Description: Once the job posting is approved, it is published.
-
End Event (Human Resources):
- Event: “Job posted”
- Description: The process ends with the job posting being published.
Flow of the Process
-
Business Department:
- The process starts with the need for a new employee.
- The Business Department reports the job opening.
-
Human Resources:
- The Human Resources Department writes the job posting.
- The job posting is reviewed.
- If the job posting is not okay, it is reworked and reviewed again.
- If the job posting is okay, it is published.
- The process ends with the job posting being published.
Key Points
- Lanes: The diagram uses lanes to separate the responsibilities of the Business Department and the Human Resources Department.
- Gateways: Exclusive gateways are used to make decisions based on the review of the job posting.
- Tasks: Specific tasks are assigned to each department to ensure the job posting process is completed efficiently.
This BPMN diagram provides a clear and structured representation of the job posting process, making it easier to understand and communicate the steps involved in posting a job.
Conclusion
BPMN provides a standardized and visual way to model business processes. By understanding and using the activity notation elements described in this guide, you can create clear and effective BPMN diagrams to represent and communicate your business processes. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced process modeler, mastering BPMN activity notation will enhance your ability to design and improve business processes.
- Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm for Business Process Modeling
- Streamlining Business Processes with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Business Process Modeling Software
- Visual Paradigm: Your Comprehensive Solution for Integrated Enterprise Modeling
- Demystifying BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
- Navigating Business Processes with BPMN: A Visual Odyssey
- Visual Paradigm: The Ultimate All-in-One Visual Modeling Platform for Enterprise Architecture and Software Design
- Top Visual Paradigm Tools for Business Process Modeling
- Visual Paradigm: The Premier Tool for ArchiMate EA Modeling
- Mastering Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tool: A Step-by-Step Learning Guide
- Simplify Business Process Modeling with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tools
- BPMN — Quick Guide
- BPMN in a Nutshell — with Free Online BPMN Tool & Examples
- A Comprehensive Guide to BPMN
- Modeling As-Is and To-Be Processes
- How to Perform Gap Analysis with BPMN?
- Visual Paradigm: A Comprehensive Suite for IT Project Development and Digital Transformation

