Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to ArchiMate: Modeling Enterprise Architecture
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to ArchiMate: Modeling Enterprise Architecture
Comprehensive Guide to ArchiMate: Modeling Enterprise Architecture
Introduction
ArchiMate is a widely recognized modeling language that provides a standardized approach for designing, describing, and analyzing enterprise architecture (EA). As organizations strive to align their IT landscape with business goals using various EA frameworks, ArchiMate plays a crucial role in facilitating effective communication and decision-making. This guide explores the fundamentals of ArchiMate, its key components, benefits, examples, and certification options.
What is ArchiMate?
ArchiMate is a graphical modeling language specifically designed for enterprise architecture. It provides a standardized notation to describe, analyze, and visualize the relationships between various architectural domains. The primary purpose of ArchiMate is to facilitate clear communication among stakeholders, support decision-making, and enable the effective management of complex IT landscapes.
History and Development
ArchiMate was initially developed by the Telematica Instituut in the Netherlands in 2002. In 2009, the Open Group, a global consortium responsible for developing open, vendor-neutral IT standards and certifications, adopted ArchiMate as a standard. Since then, ArchiMate has become one of the most popular modeling languages recognized and adopted by enterprise architects globally.
Benefits of ArchiMate
Using ArchiMate for enterprise architecture modeling and analysis offers several benefits:
- Standardization: ArchiMate provides a standardized notation and approach, enabling consistent communication and understanding among stakeholders.
- Holistic View: Its layered structure and comprehensive frameworks facilitate a holistic view of the enterprise architecture, allowing architects to identify dependencies and potential impacts across domains.
- Improved Decision-Making: With clear visualizations and a standardized language, ArchiMate supports informed decision-making and helps organizations align their IT landscape with business goals.
- Enhanced Collaboration: ArchiMate fosters collaboration among stakeholders by providing a common language and set of models that can be easily shared and understood.
Disadvantages of ArchiMate
While ArchiMate is a comprehensive modeling language, it has certain drawbacks:
- Learning Curve: The complex set of concepts and relationships can result in a steep learning curve, especially for individuals new to enterprise architecture.
- Overwhelming Complexity: The richness and complexity of ArchiMate can lead to models that become overly complex and difficult to manage.
- Lack of Industry-Specific Extensions: ArchiMate provides a generic framework, which may lack specific extensions or industry-specific concepts.
- Potential for Misinterpretation: There is a risk of misinterpretation if the models are not well-defined, necessitating clear documentation and effective communication.
Key Components of ArchiMate
Aspects
Aspects represent different perspectives or views of the enterprise architecture. ArchiMate defines four primary aspects:
- Active Structure: Focuses on subjects that can perform behavior, including actors, business roles, application components, and infrastructure elements.
- Behavior: Captures the dynamic aspects of the architecture, describing the behavior and interactions of architectural elements over time, such as processes and services.
- Passive Structure: Deals with the representation and management of data and information, including data objects and business artifacts.
- Motivation: Models the drivers, goals, principles, requirements, and stakeholders that influence the architecture.
Layers
Layers represent different levels of abstraction within the architecture. ArchiMate defines the following primary layers:
- Strategy Layer: Captures strategic aspects, including capabilities, business goals, and principles.
- Business Layer: Models business processes, actors, and products.
- Application Layer: Bridges the business and technology layers, modeling software applications and their functionalities.
- Technology Layer: Focuses on the technology infrastructure, including devices and systems software.
- Physical Layer: Incorporates physical infrastructure elements, such as servers and storage devices.
- Implementation and Migration Layer: Supports modeling transformation and change, including project portfolios and migration paths.
Relationships
ArchiMate features various relationships connecting architectural elements:
- Structural Relationships: Represent static construction, including composition, aggregation, assignment, and realization.
- Dependency Relationships: Show dependencies between elements, including used by, access, serve, and influence.
- Dynamic Relationships: Describe entity behavior or sequence, encompassing flow, triggering, and association.
Viewpoints
ArchiMate viewpoints are predefined perspectives that guide the creation of architecture views. Each viewpoint focuses on specific aspects of the architecture and highlights relevant elements and relationships. For example:
- Business Process Viewpoint: Emphasizes business processes and their dependencies.
- Application Cooperation Viewpoint: Highlights interactions between different application components.
ArchiMate Example
ArchiMate is a popular enterprise architecture modeling language that provides a standardized way to describe, analyze, and visualize the relationships among business processes, organizational structures, information flows, IT systems, and technical infrastructure.
To illustrate how ArchiMate can represent enterprise architecture, consider the following simplified example:
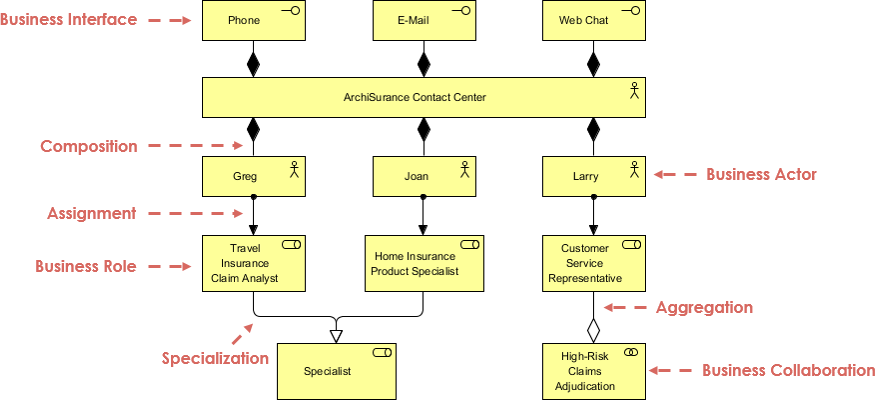
Key Concepts in the ArchiMate Example
-
Business Interface:
- Phone, E-Mail, Web Chat: These are the interfaces through which the business interacts with external entities, such as customers or other organizations. They represent the channels through which communication and data exchange occur.
-
ArchiSurance Contact Center:
- This is the central component that handles incoming communications from the business interfaces. It acts as a hub for managing customer interactions and directing them to the appropriate business actors.
-
Business Actor:
- Greg, Joan, Larry: These are individuals or roles within the organization who perform specific tasks or functions. They are assigned to different business roles based on their expertise and responsibilities.
-
Business Role:
- Travel Insurance Claim Analyst, Home Insurance Product Specialist, Customer Service Representative: These are the specific roles that business actors (Greg, Joan, Larry) are assigned to. Each role has distinct responsibilities and tasks within the organization.
-
Specialization:
- Specialist: This concept indicates that a business role can be further specialized into more specific roles. For example, a Travel Insurance Claim Analyst might specialize in certain types of claims.
-
Aggregation:
- High-Risk Claims Adjudication: This concept indicates that a business role can be part of a larger, more complex process or function. For example, a Customer Service Representative might be involved in the aggregation of high-risk claims adjudication.
-
Composition:
- This relationship shows how different elements are composed to form a larger entity. For example, the ArchiSurance Contact Center is composed of various business actors.
-
Assignment:
- This relationship indicates that a business actor is assigned to a specific business role. For example, Greg is assigned the role of Travel Insurance Claim Analyst.
-
Business Collaboration:
- This concept represents the collaboration between different business roles or actors to achieve a common goal. For example, the collaboration between a Travel Insurance Claim Analyst and a Home Insurance Product Specialist to handle complex claims.
Interpretation
The ArchiMate example illustrates how different components of an organization interact and collaborate to manage customer communications and handle specific business processes. Here’s a step-by-step interpretation:
-
Customer Communication:
- Customers interact with the ArchiSurance Contact Center through various interfaces such as phone, email, or web chat.
-
Contact Center Management:
- The ArchiSurance Contact Center receives these communications and directs them to the appropriate business actors (Greg, Joan, Larry) based on their assigned roles.
-
Role Assignment:
- Greg is assigned the role of Travel Insurance Claim Analyst.
- Joan is assigned the role of Home Insurance Product Specialist.
- Larry is assigned the role of Customer Service Representative.
-
Specialization and Aggregation:
- The Travel Insurance Claim Analyst role can be further specialized into more specific roles.
- The Customer Service Representative role can be part of a larger process, such as high-risk claims adjudication.
-
Collaboration:
- Different business roles collaborate to handle complex tasks. For example, a Travel Insurance Claim Analyst might work with a Home Insurance Product Specialist to resolve a claim that involves both travel and home insurance.
The ArchiMate example provides a clear and structured way to visualize and understand the relationships and interactions within an organization. It helps in identifying the roles, responsibilities, and collaborations necessary to manage business processes effectively. This model can be used for analysis, planning, and improvement of enterprise architecture.
ArchiMate Certifications and Training
To effectively use ArchiMate, professionals can pursue various certification levels offered by The Open Group:
- ArchiMate 3 Foundation (Level 1): This certification covers the basic concepts and principles of ArchiMate, including its core framework and notation.
- ArchiMate 3 Practitioner (Level 2): This certification is aimed at individuals who want to demonstrate their ability to apply ArchiMate in practice, including modeling and analyzing enterprise architecture.
Training programs are available through various providers, including online courses, workshops, and seminars, to help professionals gain the necessary skills and knowledge.
ArchiMate and TOGAF
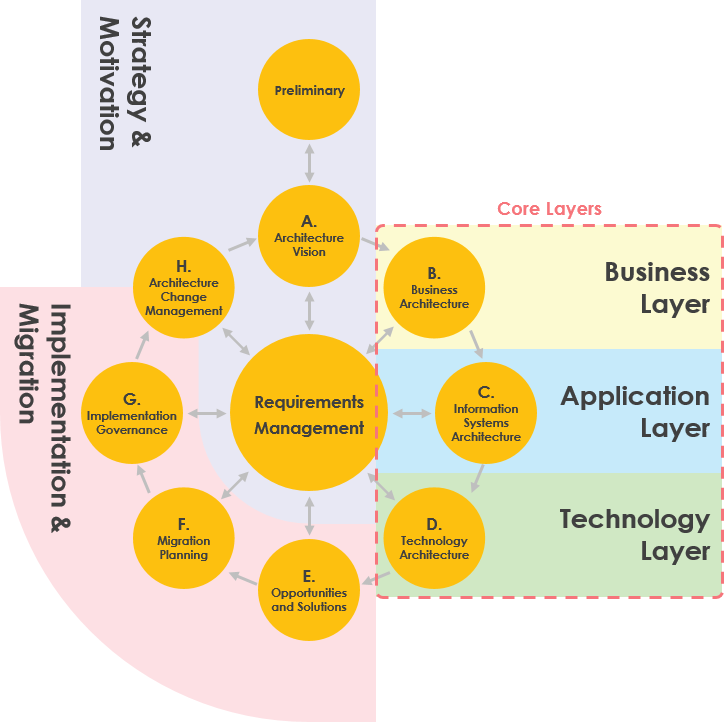
ArchiMate and TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) are both frameworks commonly used in enterprise architecture, but they serve different purposes:
- Focus: ArchiMate is a modeling language that provides a standardized notation for visualizing enterprise architecture, while TOGAF is a broader framework that includes a methodology, templates, and tools for developing and managing architecture.
- Scope: ArchiMate focuses on visual modeling and representation, whereas TOGAF encompasses the entire architecture development process, from planning to implementation.
- Notation: ArchiMate provides a specific notation for visualizing architecture, while TOGAF offers guidance on creating multiple views and perspectives.
- Level of Detail: Both frameworks include high-level and detailed views of architecture, emphasizing alignment with business strategy.
- Implementation: TOGAF provides guidance on implementing architecture, including developing roadmaps and managing projects, while ArchiMate primarily focuses on modeling and representation.
Recommended Modeling Tool
Visual Paradigm is a highly recommended tool for both TOGAF and ArchiMate, offering a comprehensive suite of features that support enterprise architecture development and modeling. Here are some key reasons why Visual Paradigm stands out:

-
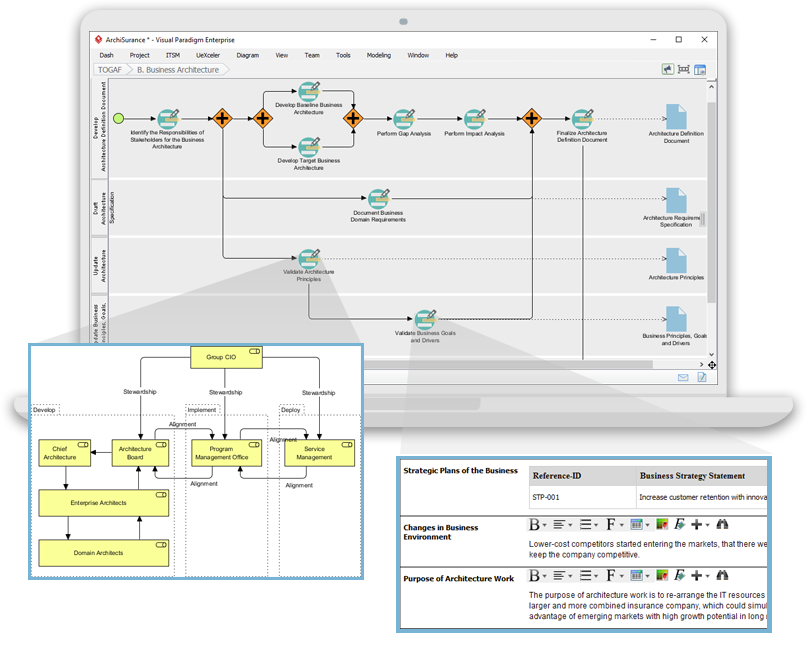
Integration with TOGAF ADM: Visual Paradigm is fully integrated with the TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM), providing a structured approach to developing enterprise architectures. It includes a process navigator that guides users through the execution and completion of TOGAF ADM phases, activities, and steps, making it easier to follow the framework’s best practices1.

-
ArchiMate 3.1 Support: The tool is certified by The Open Group for ArchiMate 3.1, ensuring that it meets the standards for creating ArchiMate models and diagrams. This certification guarantees that the tool is reliable and aligned with the latest ArchiMate specifications1.
-
Comprehensive Diagramming and Analysis Tools: Visual Paradigm offers a wide range of diagramming and analysis tools, including ArchiMate 3.1 diagrams, viewpoints, Implementation Plan Diagrams, Migration Roadmaps, Maturity Analysis, PERT Charts, RACI Charts, and more. These tools help in analyzing and documenting enterprise architectures effectively1.
-
User-Friendly Interface: The tool is designed to be user-friendly, with features like color-coding for elements in diagrams, which makes it easier to visualize and manage complex architectures. It also provides samples and instructions to help users understand and apply TOGAF and ArchiMate concepts1.
-
Affordable and Award-Winning: Visual Paradigm is recognized as an international award-winning tool, offering incredible features at an affordable price. This makes it accessible to a wide range of organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises1.
-
Collaboration and Customization: Visual Paradigm supports global collaboration and offers customizable dashboards, impact analysis, and automated analytics. These features enhance teamwork and allow for tailored solutions that meet specific organizational needs.
Conclusion
ArchiMate is a powerful and standardized modeling language that plays a vital role in enterprise architecture. Its structured approach, comprehensive frameworks, and clear visualizations facilitate effective communication, decision-making, and collaboration among stakeholders. While it has certain drawbacks, such as a steep learning curve and potential complexity, the benefits it offers in terms of standardization and holistic views make it an invaluable tool for enterprise architects.
By understanding the key components, relationships, and viewpoints of ArchiMate, professionals can leverage this modeling language to create meaningful representations of their enterprise architecture, ultimately aligning IT landscapes with business goals. With certification options available, individuals can enhance their skills and contribute effectively to their organizations’ architectural endeavors.
TOGAF and ArchiMate Reference
Resources
- Visual Paradigm TOGAF – Everything about TOGAF, Enterprise Architecture, ArchiMate, and more
- Visual Paradigm. (n.d.). Visual Paradigm TOGAF – Everything about TOGAF, Enterprise Architecture, ArchiMate, and more .
- TOGAF® Tool for Enterprise Architecture – ArchiMetric
- ArchiMetric. (2022, February 22). TOGAF® Tool for Enterprise Architecture – ArchiMetric .
- ArchiMate diagram in Visual Paradigm
- Visual Paradigm. (n.d.). ArchiMate diagram in Visual Paradigm .
- Modelling interfaces between applications in ArchiMate and Visual Paradigm – Stack Overflow
- Stack Overflow. (n.d.). Modelling interfaces between applications in ArchiMate and Visual Paradigm – Stack Overflow .
- Mastering Enterprise Architecture with Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF Tool – ArchiMetric
- ArchiMetric. (2024, December 9). Mastering Enterprise Architecture with Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF Tool – ArchiMetric .
- Using ArchiMate Tool with TOGAF ADM
- Visual Paradigm. (n.d.). Using ArchiMate Tool with TOGAF ADM .
- Visual Paradigm – Requirements.com
- Requirements.com. (2022, June 19). Visual Paradigm – Requirements.com .
- Free Online ArchiMate Tool + Examples – Cybermediana
- Cybermediana. (2022, February 25). Free Online ArchiMate Tool + Examples – Cybermediana .
- ArchiMate 3: A Comprehensive Overview – Cybermedian
- Cybermedian. (2024, October 23). ArchiMate 3: A Comprehensive Overview – Cybermedian .
- ArchiMate® 3: A Comprehensive Overview – Cybermedian
- Cybermedian. (2024, October 23). ArchiMate® 3: A Comprehensive Overview – Cybermedian .

