Now Reading: Mastering BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
-
01
Mastering BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
Mastering BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
Introduction
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a powerful tool for visualizing, analyzing, and improving business processes. It provides a standardized graphical notation that is easily understood by all stakeholders, from business analysts to technical developers. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key concepts of BPMN, offer practical tips and tricks, and provide guidelines for creating effective BPMN diagrams.
Key Concepts of BPMN
1. Flow Objects
Flow objects are the core elements that define the behavior of a business process. They include:

BPMN Notation
-
Events: Represented by circles, events indicate something that happens during the process. There are three types:
- Start Event: Marks the beginning of a process.
- Intermediate Event: Occurs between activities and can influence the flow of the process.
- End Event: Marks the completion of a process.
-
Activities: Represented by rounded rectangles, activities are tasks performed within the process. There are two types:
- Task: A single unit of work.
- Sub-Process: A process within a process, which can be expanded to show more detailed steps.
-
Gateways: Represented by diamonds, gateways control the flow of the process based on conditions. Types include:
- Exclusive Gateway: Allows only one path to be taken.
- Inclusive Gateway: Allows multiple paths to be taken.
- Parallel Gateway: Allows multiple paths to be taken simultaneously.
2. Connecting Objects
Connecting objects define the relationships between flow objects:
- Sequence Flow: Shows the order of activities within the same pool, represented by a solid line with an arrowhead.
- Message Flow: Depicts the exchange of messages between different pools, represented by a dashed line with an arrowhead.
- Association: Connects artifacts to flow objects using a dotted line.
3. Swimlanes
Swimlanes visually represent the participants or roles involved in the process:
- Pools: Represent major participants in a process, often different organizations or departments.
- Lanes: Represent individual roles or departments within a pool.
4. Artifacts
Artifacts provide additional context without affecting the flow:
- Data Object: Represents information used or produced during the process.
- Group: Visually groups related activities.
- Text Annotation: Adds descriptive text to the diagram.
Tips and Tricks for Effective BPMN Modeling
-
Keep It Simple: Start with a simple diagram and gradually add details as needed. Avoid overcomplicating the diagram with unnecessary elements.
-
Use Standard Symbols: Stick to the standard BPMN symbols to ensure clarity and consistency. This makes the diagram easier to understand for all stakeholders.
-
Focus on Key Activities: Identify the key activities and decision points in the process. These are the most important elements to include in your diagram.
-
Validate with Stakeholders: Regularly validate your diagram with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness. Their input can provide valuable insights and help identify any missing steps or errors.
-
Document Assumptions: Clearly document any assumptions or constraints that apply to the process. This helps in understanding the context and limitations of the diagram.
-
Use Annotations: Add annotations to provide additional information or clarify specific parts of the diagram. This can be particularly useful for complex processes.
Guidelines for Creating BPMN Diagrams
-
Define the Scope: Clearly define the scope of the process you are modeling. This includes identifying the start and end points, as well as the key activities and decision points.
-
Identify Participants: Identify the participants involved in the process and create pools and lanes accordingly. This helps in understanding the roles and responsibilities of each participant.
-
Use Events Wisely: Use events to trigger the start and end of the process, as well as to influence the flow of activities. Ensure that events are clearly defined and logically placed within the diagram.
-
Sequence Activities: Arrange the activities in a logical sequence, using gateways to control the flow based on conditions. Ensure that the sequence flow is clear and easy to follow.
-
Communicate Effectively: Use message flows to show the communication between different participants. Ensure that message flows are clearly defined and logically placed within the diagram.
-
Review and Refine: Regularly review and refine your diagram to ensure accuracy and completeness. Incorporate feedback from stakeholders and make necessary adjustments as needed.
BPMN Example – Medical System
This diagram is a Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) representation of a surgical process within a hospital setting. It illustrates the sequence of activities from the arrival of a patient to the completion of the surgical procedure and subsequent discharge. Here’s a detailed explanation and interpretation of the diagram:
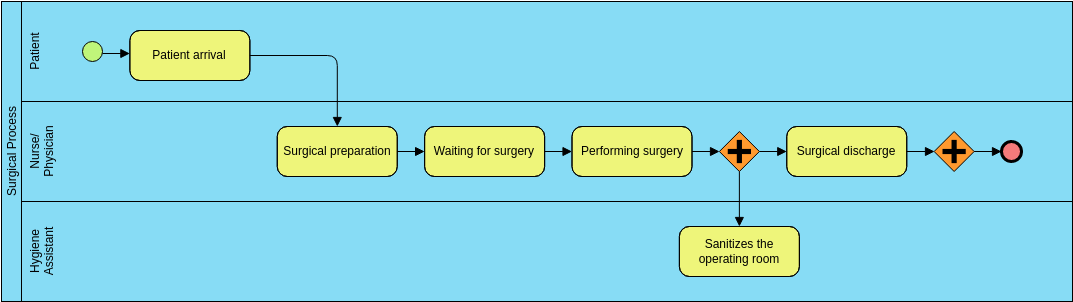
BPMN Example – Medical System
Key Components:
-
Pools and Lanes:
- Pools: Represent major participants in a process. In this diagram, there are three pools: “Patient,” “Surgical Process Physician,” and “Hygiene Assistant.”
- Lanes: Subdivisions within a pool that represent different roles or departments. Each pool here represents a different role in the surgical process.
-
Events:
- Start Event: Indicated by a yellow circle, this event triggers the start of the process. In this case, it is the “Patient arrival.”
- End Event: Indicated by a red circle, this event marks the completion of the process.
-
Tasks:
- Represented by rounded rectangles, tasks are activities performed within the process.
- Surgical Process Physician:
- Surgical Preparation: The physician prepares for the surgery.
- Waiting for Surgery: The physician waits for the surgery to begin.
- Performing Surgery: The physician performs the surgery.
- Surgical Discharge: The physician discharges the patient post-surgery.
- Hygiene Assistant:
- Sanitizes the Operating Room: The hygiene assistant sanitizes the operating room after the surgery.
-
Gateways:
- Represented by diamond shapes, gateways control the flow of the process based on conditions.
- Exclusive Gateway: Indicated by a diamond with an “X,” this gateway allows only one path to be taken. In this diagram, it is used to determine the flow after performing the surgery.
-
Sequence Flow:
- Indicated by solid arrows, sequence flows show the order of activities within the process.
- The sequence flow starts from the “Patient arrival” event, moves through the tasks and gateways, and ends at the “End” event.
Process Flow:
-
Patient Arrival:
- The process begins when the patient arrives at the hospital.
-
Surgical Preparation:
- The surgical process physician prepares for the surgery.
-
Waiting for Surgery:
- The physician waits for the surgery to begin.
-
Performing Surgery:
- The physician performs the surgery.
-
Exclusive Gateway:
- After performing the surgery, the process flow is controlled by an exclusive gateway. This gateway determines the next steps based on certain conditions.
-
Surgical Discharge:
- If the conditions are met, the physician discharges the patient post-surgery.
-
Sanitizes the Operating Room:
- Concurrently, the hygiene assistant sanitizes the operating room after the surgery.
-
End Event:
- The process ends after the surgical discharge and sanitization of the operating room.
Interpretation:
This BPMN diagram provides a clear visual representation of the surgical process within a hospital. It helps in understanding the flow of activities, decision points, and the roles involved in the surgical procedure. The diagram highlights the interactions between the patient, the surgical process physician, and the hygiene assistant, ensuring that all necessary steps are followed for a successful surgical outcome.
Key Points:
- Clarity and Communication: The diagram effectively communicates the sequence of activities and the roles involved, making it easier for all stakeholders to understand the process.
- Process Improvement: By visualizing the surgical process, potential areas for improvement can be identified, such as reducing waiting times or enhancing hygiene protocols.
- Standardization: The use of standard BPMN symbols ensures consistency and clarity, making the diagram easily understandable by anyone familiar with BPMN.
In summary, this BPMN diagram is a valuable tool for documenting and analyzing the surgical process, helping to ensure that all steps are followed correctly and efficiently.
Conclusion
BPMN is a powerful tool for visualizing and documenting business processes. By understanding the key concepts and following best practices, you can create effective BPMN diagrams that help in analyzing and improving business processes. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of BPMN, along with practical tips and guidelines to enhance your modeling skills. With practice and the insights provided, you can become proficient in creating BPMN diagrams that add value to your organization.


