Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to BPMN Swimlanes Notation
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to BPMN Swimlanes Notation
Comprehensive Guide to BPMN Swimlanes Notation
Introduction
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized method for visualizing business processes. Swimlanes are a key component of BPMN, used to organize and categorize activities within a process model. This guide will provide a detailed explanation of swimlanes, their usage, and best practices, along with numerous examples to illustrate their application.
What are Swimlanes?
Swimlanes are visual elements in BPMN that represent participants, roles, or systems involved in a process. They help in organizing and categorizing activities, making the process model more readable and understandable. Swimlanes can be horizontal or vertical and are divided into pools and lanes.
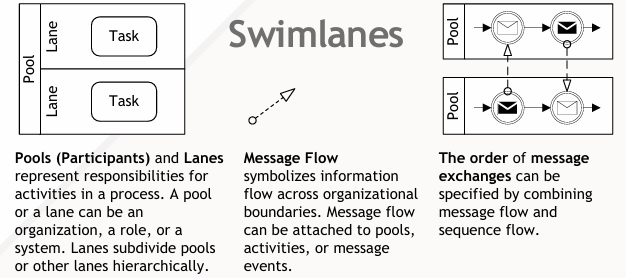
Pools
A pool represents a major participant in a process, such as an organization, a department, or a system. Pools are typically used to separate different participants in a collaboration diagram.
Lanes
Lanes are subdivisions within a pool and represent roles, sub-processes, or systems within a participant. Lanes help in further categorizing activities within a pool.
Key Concepts
Participants
Participants are the entities involved in the process. They can be organizations, departments, roles, or systems. Each participant is represented by a pool in the BPMN diagram.
Activities
Activities are the tasks or actions performed within a process. They are placed within lanes to show which participant or role is responsible for each task.
Message Flow
Message flow represents the communication between participants. It is depicted as a dashed arrow connecting activities in different pools or lanes.
Sequence Flow
Sequence flow represents the order of activities within a process. It is depicted as a solid arrow connecting activities within the same pool or lane.
Guidelines for Using Swimlanes
1. Identify Participants
Determine the key participants in the process. Each participant should have its own pool.
2. Define Pools and Lanes
Create a pool for each participant. Within each pool, define lanes to represent roles, sub-processes, or systems.
3. Place Activities in Lanes
Place activities within the appropriate lanes to show which participant or role is responsible for each task.
4. Use Message Flow for Communication
Use message flow to represent communication between participants. Connect activities in different pools or lanes with dashed arrows.
5. Use Sequence Flow for Order
Use sequence flow to represent the order of activities within a process. Connect activities within the same pool or lane with solid arrows.
Examples
This diagram represents a business process for order fulfillment using Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). It illustrates the interaction between different departments within an organization to fulfill an order. Let’s break down and interpret each part of the diagram:
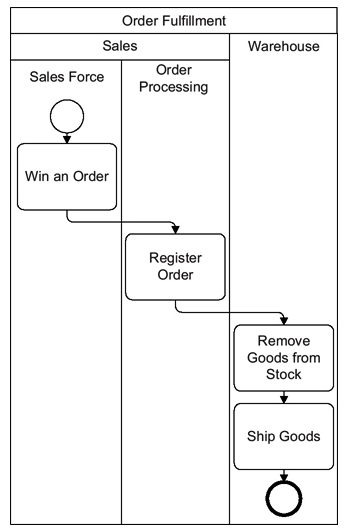
Pool: Order Fulfillment
The entire process is contained within a pool named “Order Fulfillment,” which represents the overall scope of the process.
Lanes
The pool is divided into two lanes: Sales and Warehouse. Lanes are used to organize activities within the pool and represent different departments or roles involved in the process.
Sales Lane
-
Sales Force
- Win an Order: This is the starting event for the process, represented by a circle with a single border. It indicates that the sales force has successfully won an order from a customer.
-
Order Processing
- Register Order: This task involves registering the order details into the system. It is represented by a rounded rectangle, which denotes a task or activity.
Warehouse Lane
-
Remove Goods from Stock
- This task involves removing the ordered goods from the warehouse stock. It is represented by a rounded rectangle.
-
Ship Goods
- This is the final task in the process, where the goods are shipped to the customer. It is represented by a rounded rectangle.
- The process ends with a circle with a bold border, indicating the end event of the process.
Sequence Flow
The sequence flow is represented by solid arrows connecting the tasks. It shows the order in which the activities are performed:
- The process starts with the “Win an Order” event in the Sales Force lane.
- The order is then registered in the “Register Order” task within the Order Processing lane.
- The registered order triggers the “Remove Goods from Stock” task in the Warehouse lane.
- Finally, the goods are shipped in the “Ship Goods” task, marking the end of the process.
Interpretation
This BPMN diagram provides a clear and structured representation of the order fulfillment process. It shows how different departments (Sales and Warehouse) collaborate to fulfill an order. The process starts with the sales team winning an order, followed by order registration, removal of goods from stock, and finally shipping the goods to the customer.
Key Points
- Pools and Lanes: The diagram uses pools and lanes to organize activities by department, making it easy to understand the roles and responsibilities of each department.
- Events and Tasks: The diagram includes start and end events, as well as tasks represented by rounded rectangles.
- Sequence Flow: The solid arrows indicate the sequence of activities, showing the flow of the process from start to finish.
This diagram is a useful tool for visualizing and understanding the order fulfillment process, helping stakeholders to identify potential bottlenecks, improve efficiency, and ensure smooth collaboration between departments.
Tips and Tricks
1. Keep It Simple
Start with a simple model and gradually add details. This helps in understanding the basic flow before diving into complexities.
2. Use Descriptive Labels
Use clear and descriptive labels for activities, events, and message objects. This makes the model easier to understand.
3. Validate the Model
Regularly validate the model with stakeholders to ensure it accurately represents the real-world process.
4. Consider Edge Cases
Think about edge cases and exceptions. For example, what happens if an order is canceled?
5. Use Tools
Use modeling tools to create and manage your BPMN diagrams. Tools like Bizagi Modeler, Signavio, or Microsoft Visio can be helpful.
Conclusion
Swimlanes are a powerful tool in BPMN for organizing and categorizing activities within a process model. By following the guidelines and tips outlined in this guide, you can create effective BPMN diagrams that represent the interactions between different participants, roles, or systems. The examples provided illustrate how to apply these concepts in various scenarios.
BPMN References
- Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm for Business Process Modeling
- Streamlining Business Processes with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Business Process Modeling Software
- Visual Paradigm: Your Comprehensive Solution for Integrated Enterprise Modeling
- Demystifying BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
- Navigating Business Processes with BPMN: A Visual Odyssey
- Visual Paradigm: The Ultimate All-in-One Visual Modeling Platform for Enterprise Architecture and Software Design
- Top Visual Paradigm Tools for Business Process Modeling
- Visual Paradigm: The Premier Tool for ArchiMate EA Modeling
- Mastering Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tool: A Step-by-Step Learning Guide
- Simplify Business Process Modeling with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tools
- BPMN — Quick Guide
- BPMN in a Nutshell — with Free Online BPMN Tool & Examples
- A Comprehensive Guide to BPMN
- Modeling As-Is and To-Be Processes
- How to Perform Gap Analysis with BPMN?
- Visual Paradigm: A Comprehensive Suite for IT Project Development and Digital Transformation

