Now Reading: BPMN Comprehensive Guide to Business-To-Business Collaboration Modeling
-
01
BPMN Comprehensive Guide to Business-To-Business Collaboration Modeling
BPMN Comprehensive Guide to Business-To-Business Collaboration Modeling
Introduction
Business-To-Business (B2B) collaboration involves the interaction between different organizations to achieve common goals. Modeling these interactions is crucial for understanding and optimizing business processes. This guide will walk you through the key concepts, guidelines, and tips for effective B2B collaboration modeling, using a pizza ordering process as an example.
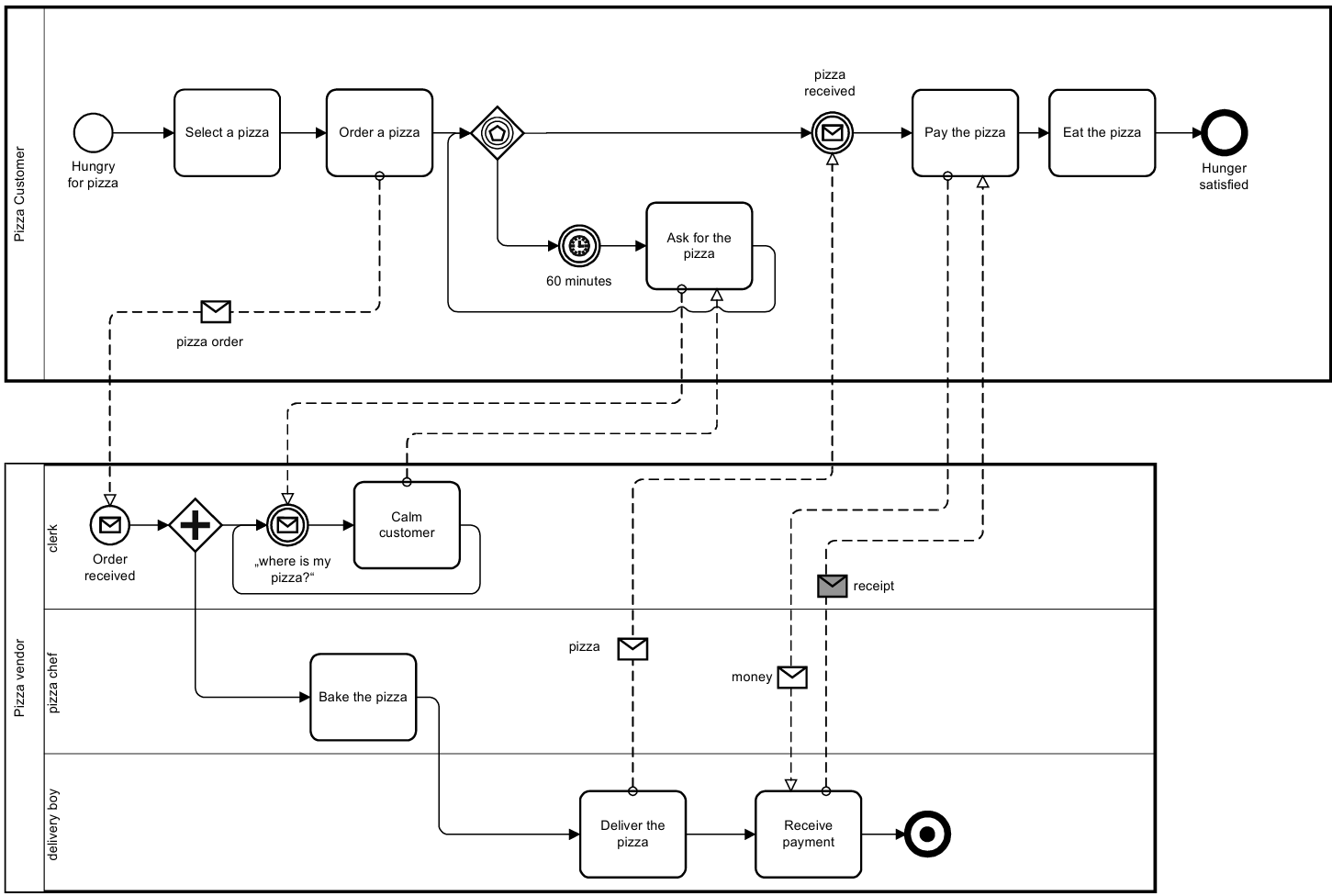
BPMN Example – Order Fulfillment and Procurement
Key Concepts
Participants and Pools
In B2B collaboration modeling, participants are the different organizations or departments involved in the process. Each participant is represented by a dedicated pool, which contains the activities and events specific to that participant.
Events and Gateways
Events trigger the start or continuation of a process. Gateways control the flow of the process based on conditions or events. In our example, an event-based gateway is used to handle the customer’s wait for the pizza delivery.
Message Flows
Message flows represent the communication between participants. They can carry informational objects (like orders) or physical objects (like the pizza or money).
Guidelines for B2B Collaboration Modeling
1. Identify Participants
Determine the key participants in the collaboration. In our example, the participants are the pizza customer and the pizza vendor.
2. Define Pools and Lanes
Create a pool for each participant. Within each pool, use lanes to represent different roles or departments. For the pizza vendor, we have lanes for the clerk, pizza chef, and delivery boy.
3. Model the Process Flow
Start with the initial event and model the sequence of activities and events for each participant. Use message flows to show interactions between participants.
4. Use Gateways for Decision Points
Use gateways to model decision points or branches in the process. In our example, an event-based gateway is used to handle the customer’s wait for the pizza delivery.
5. Include Message Objects
Use message objects to represent the information or physical objects exchanged between participants. In our example, message objects include the pizza order, the pizza, and the money.
Tips and Tricks
1. Keep It Simple
Start with a simple model and gradually add details. This helps in understanding the basic flow before diving into complexities.
2. Use Descriptive Labels
Use clear and descriptive labels for activities, events, and message objects. This makes the model easier to understand.
3. Validate the Model
Regularly validate the model with stakeholders to ensure it accurately represents the real-world process.
4. Consider Edge Cases
Think about edge cases and exceptions. For example, what happens if the pizza is not delivered within 60 minutes?
5. Use Tools
Use modeling tools to create and manage your B2B collaboration models. Tools like Bizagi Modeler, Signavio, or Microsoft Visio can be helpful.
Example: Pizza Ordering Process
Introduction
Business-To-Business (B2B) collaboration involves the interaction between different organizations to achieve common goals. Modeling these interactions is crucial for understanding and optimizing business processes. This guide will walk you through the key concepts, guidelines, and tips for effective B2B collaboration modeling, using a pizza ordering process as an example.
Key Concepts
Participants and Pools
In B2B collaboration modeling, participants are the different organizations or departments involved in the process. Each participant is represented by a dedicated pool, which contains the activities and events specific to that participant.
Events and Gateways
Events trigger the start or continuation of a process. Gateways control the flow of the process based on conditions or events. In our example, an event-based gateway is used to handle the customer’s wait for the pizza delivery.
Message Flows
Message flows represent the communication between participants. They can carry informational objects (like orders) or physical objects (like the pizza or money).
Guidelines for B2B Collaboration Modeling
1. Identify Participants
Determine the key participants in the collaboration. In our example, the participants are the pizza customer and the pizza vendor.
2. Define Pools and Lanes
Create a pool for each participant. Within each pool, use lanes to represent different roles or departments. For the pizza vendor, we have lanes for the clerk, pizza chef, and delivery boy.
3. Model the Process Flow
Start with the initial event and model the sequence of activities and events for each participant. Use message flows to show interactions between participants.
4. Use Gateways for Decision Points
Use gateways to model decision points or branches in the process. In our example, an event-based gateway is used to handle the customer’s wait for the pizza delivery.
5. Include Message Objects
Use message objects to represent the information or physical objects exchanged between participants. In our example, message objects include the pizza order, the pizza, and the money.
Tips and Tricks
1. Keep It Simple
Start with a simple model and gradually add details. This helps in understanding the basic flow before diving into complexities.
2. Use Descriptive Labels
Use clear and descriptive labels for activities, events, and message objects. This makes the model easier to understand.
3. Validate the Model
Regularly validate the model with stakeholders to ensure it accurately represents the real-world process.
4. Consider Edge Cases
Think about edge cases and exceptions. For example, what happens if the pizza is not delivered within 60 minutes?
5. Use Tools
Use modeling tools to create and manage your B2B collaboration models. Tools like Bizagi Modeler, Signavio, or Microsoft Visio can be helpful.
Example: Pizza Ordering Process

Pizza Customer Pool
- Hungry for pizza: The process starts when the customer is hungry.
- Select a pizza: The customer selects a pizza.
- Order a pizza: The customer orders the pizza.
- Event-based Gateway: The customer waits for the pizza delivery or 60 minutes.
- Ask for the pizza: If the pizza is not delivered within 60 minutes, the customer asks for the pizza.
- Pizza received: The customer receives the pizza.
- Pay the pizza: The customer pays for the pizza.
- Eat the pizza: The customer eats the pizza.
- Hunger satisfied: The process ends with the customer’s hunger satisfied.
Pizza Vendor Pool
- Order received: The process starts when the order is received.
- Calm customer: The clerk calms the customer if they ask for the pizza.
- Bake the pizza: The pizza chef bakes the pizza.
- Deliver the pizza: The delivery boy delivers the pizza.
- Receive payment: The delivery boy receives the payment and gives a receipt.
Message Flows
- Pizza order: From the customer to the vendor.
- Pizza: From the vendor to the customer.
- Money: From the customer to the vendor.
- Receipt: From the vendor to the customer.
Conclusion
B2B collaboration modeling is a powerful tool for understanding and optimizing business processes. By following the guidelines and tips outlined in this guide, you can create effective models that represent the interactions between different organizations or departments. The pizza ordering process example illustrates how to apply these concepts in a real-world scenario.
- Mastering Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tool: A Step-by-Step Learning Guide
- Simplify Business Process Modeling with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Tools
- BPMN — Quick Guide
- BPMN in a Nutshell — with Free Online BPMN Tool & Examples
- A Comprehensive Guide to BPMN
- Modeling As-Is and To-Be Processes
- How to Perform Gap Analysis with BPMN?
- Visual Paradigm: A Comprehensive Suite for IT Project Development and Digital Transformation
- Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm for Business Process Modeling
- Streamlining Business Processes with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN Business Process Modeling Software
- Visual Paradigm: Your Comprehensive Solution for Integrated Enterprise Modeling
- Demystifying BPMN: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Process Modeling
- Navigating Business Processes with BPMN: A Visual Odyssey
- Visual Paradigm: The Ultimate All-in-One Visual Modeling Platform for Enterprise Architecture and Software Design
- Top Visual Paradigm Tools for Business Process Modeling
- Visual Paradigm: The Premier Tool for ArchiMate EA Modeling
- Introduction to BPMN Part I – Visual Paradigm
- BPMN Tutorial with Example – The Leave Application Process
- How to Draw BPMN Diagram?
- BPMN Activity Types Explained
- How to Create BPMN Diagram?
- How to Develop As-Is and To-Be Business Process?
- How to Draw BPMN 2.0 Business Process Diagram?
- Introduction to BPMN Part IV – Data and Artifacts
- Introduction to BPMN Part III – Flow and Connecting Objects
- How to Draw BPMN Conversation Diagram?
- Business Process Diagram Example: Sequence
- Business Process Diagram Example: The Nobel Prize

