Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to PEST Analysis: A Case Study – Automotive Industry
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to PEST Analysis: A Case Study – Automotive Industry
Comprehensive Guide to PEST Analysis: A Case Study – Automotive Industry
Introduction to PEST Analysis
PEST analysis is a strategic tool used to evaluate the external macro-environmental factors that impact an organization or industry. The acronym PEST stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors. This analysis helps businesses understand the broader landscape in which they operate, enabling them to make informed decisions and adapt strategies in response to changing circumstances.
Case Study: PEST Analysis for the Automotive Industry
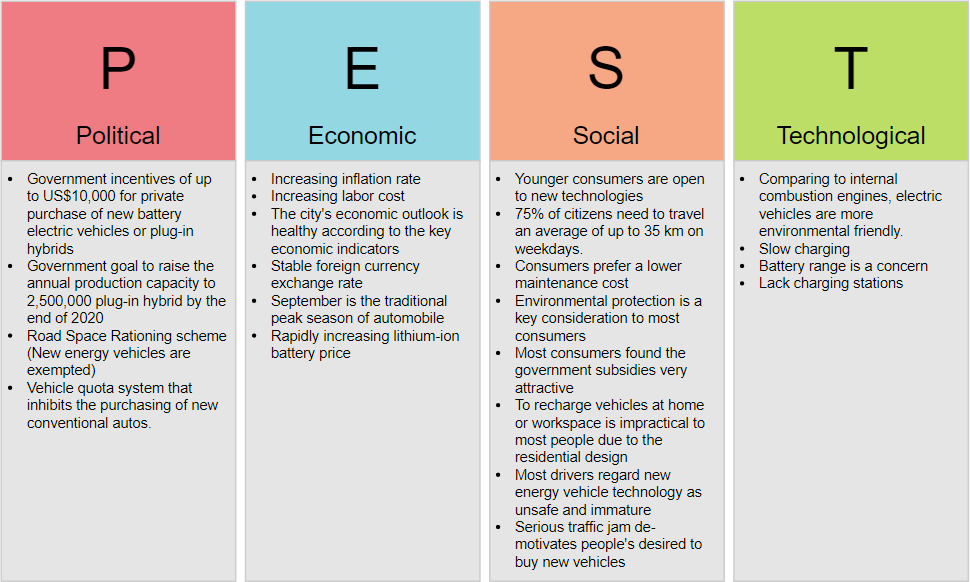
The attached infographic provides a detailed PEST analysis for the automotive industry. Let’s break down each component and explore the key concepts.
1. Political Factors
Political factors refer to the government policies, regulations, and political stability that can impact an industry. In the automotive sector, key political factors include:
- Government Incentives: Incentives of up to US$10,000 for the private purchase of new battery electric vehicles or plug-in hybrids.
- Government Goals: Aim to raise the annual production capacity to 2,500,000 plug-in hybrids by the end of 2020.
- Road Space Rationing: Schemes that exempt new energy vehicles, encouraging their adoption.
- Vehicle Quota System: Restrictions on purchasing new conventional autos, pushing consumers towards electric vehicles.
These political factors significantly influence the market dynamics by promoting the adoption of electric vehicles and reducing the demand for conventional autos.
2. Economic Factors
Economic factors encompass the economic conditions, trends, and market dynamics that affect an industry. For the automotive sector, key economic factors include:
- Inflation Rate: Increasing inflation can impact consumer purchasing power.
- Labor Cost: Rising labor costs affect the production expenses of automotive manufacturers.
- Economic Outlook: The city’s economic outlook is healthy according to key economic indicators, suggesting a stable market.
- Foreign Currency Exchange Rate: Stable exchange rates provide predictability for international trade.
- Seasonal Trends: September is traditionally the peak season for automobile sales.
- Lithium-Ion Battery Price: Rapidly increasing prices of lithium-ion batteries can affect the cost of electric vehicles.
These economic factors play a crucial role in shaping the market demand and supply dynamics, influencing the pricing and profitability of automotive products.
3. Social Factors
Social factors involve the societal attitudes, demographic shifts, and cultural trends that influence consumer behavior. In the automotive industry, key social factors include:
- Consumer Preferences: Younger consumers are open to new technologies and prefer lower maintenance costs.
- Travel Needs: 75% of citizens need to travel an average of up to 35 km on weekdays, influencing the demand for efficient vehicles.
- Environmental Protection: A key consideration for most consumers, driving the demand for eco-friendly vehicles.
- Government Subsidies: Most consumers find government subsidies very attractive, further promoting the adoption of electric vehicles.
- Charging Infrastructure: The impracticality of recharging vehicles at home or the workplace is a significant barrier for many consumers.
- Technology Perception: Most drivers regard new energy vehicle technology as unsafe and immature, affecting their willingness to adopt.
- Traffic Conditions: Serious traffic jams demotivate people’s desire to buy new vehicles, impacting market demand.
These social factors shape consumer preferences and behaviors, influencing the market demand for different types of vehicles.
4. Technological Factors
Technological factors encompass the technological advancements and innovations that impact an industry. In the automotive sector, key technological factors include:
- Environmental Friendliness: Electric vehicles are more environmentally friendly compared to internal combustion engines.
- Charging Speed: Slow charging is a concern for consumers, affecting the convenience of electric vehicles.
- Battery Range: Limited battery range is a significant concern, impacting the practicality of electric vehicles.
- Charging Infrastructure: The lack of charging stations poses a challenge for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
These technological factors influence the development and adoption of new technologies in the automotive industry, shaping the market landscape.
Summary of PEST Analysis Findings for the Automotive Industry
| Factor | Key Findings | Impact on Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Political | – Government incentives up to US$10,000 for electric vehicles. | – Promotes adoption of electric vehicles. |
| – Government goal to raise production capacity to 2,500,000 plug-in hybrids. | – Increases focus on electric vehicle production. | |
| – Road space rationing exempts new energy vehicles. | – Encourages purchase of electric vehicles. | |
| – Vehicle quota system inhibits purchasing of new conventional autos. | – Reduces demand for conventional vehicles. | |
| Economic | – Increasing inflation rate and labor cost. | – Affects consumer purchasing power and production costs. |
| – Healthy economic outlook and stable foreign currency exchange rate. | – Provides market stability and predictability. | |
| – September as the traditional peak season for automobile sales. | – Influences sales strategies and inventory management. | |
| – Rapidly increasing lithium-ion battery price. | – Impacts the cost and affordability of electric vehicles. | |
| Social | – Younger consumers open to new technologies and prefer lower maintenance. | – Drives demand for technologically advanced and low-maintenance vehicles. |
| – Consumers need to travel up to 35 km on weekdays. | – Influences demand for efficient and reliable vehicles. | |
| – Environmental protection is a key consideration. | – Increases demand for eco-friendly vehicles. | |
| – Government subsidies are attractive to consumers. | – Promotes adoption of electric vehicles. | |
| – Impracticality of recharging vehicles at home or workplace. | – A barrier to electric vehicle adoption. | |
| – Perception of new energy vehicle technology as unsafe and immature. | – Affects consumer willingness to adopt electric vehicles. | |
| – Serious traffic jams demotivate new vehicle purchases. | – Impacts overall market demand for new vehicles. | |
| Technological | – Electric vehicles are more environmentally friendly. | – Promotes shift towards electric vehicles. |
| – Slow charging and limited battery range are concerns. | – Affects convenience and practicality of electric vehicles. | |
| – Lack of charging stations. | – Hinders widespread adoption of electric vehicles. |
This table summarizes the key findings from the PEST analysis and their impacts on the automotive industry, providing a clear overview of the external factors influencing the market.
Conclusion
The PEST analysis framework provides a comprehensive understanding of the external macro-environmental factors impacting the automotive industry. By examining the political, economic, social, and technological factors, businesses can make informed decisions, adapt their strategies, and navigate the changing market dynamics effectively. The case study based on the attached infographic highlights the key concepts of PEST analysis and their practical applications in the automotive sector.


